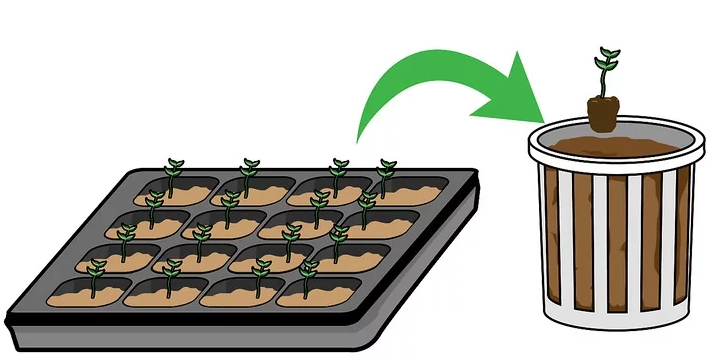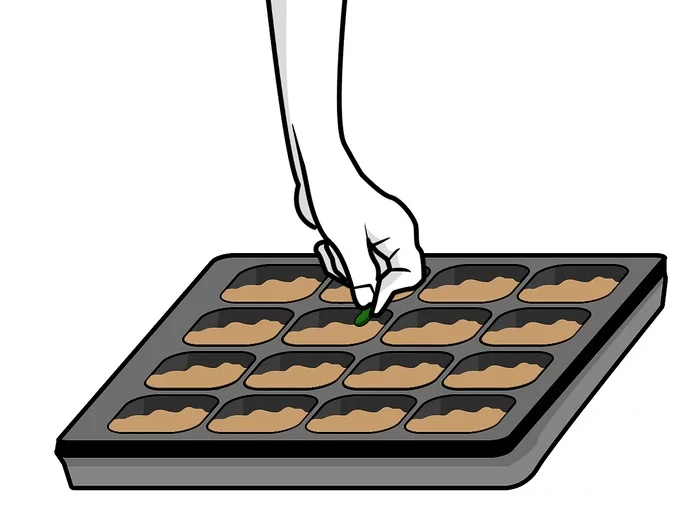
Germination
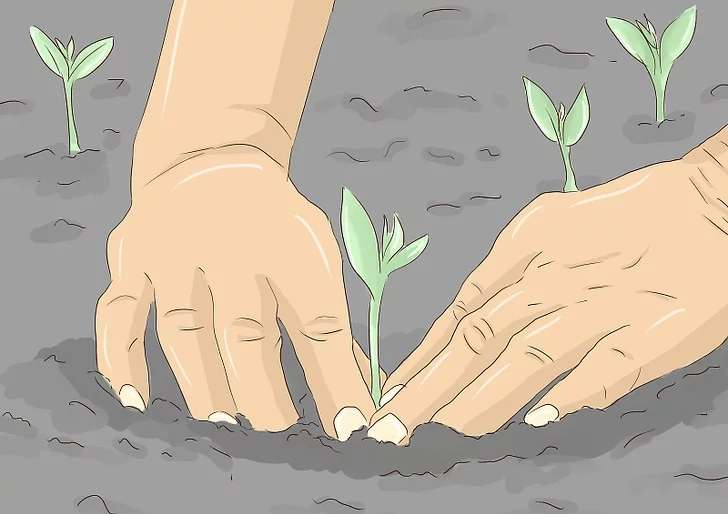
Germination is usually the growth of a plant contained within a seed; it results in the formation of the seedling. It is also the process of reactivation of metabolic machinery of the seed resulting in the emergence of radicle and plumule. Therefore, understanding the molecular aspects of seed dormancy and germination is of a great significance for the improvement of crop yield and quality.