How to Properly Transplant Seedlings

Step 1: Transfer germinated seedlings
When the true leaves (3 or 4 leave s) is seen, the plant is ready for transplant. The following requirement is Sponge, mesh pot.
Procedure: cut and trim sponge that suit to the mesh pot, after trimming sponge, cut straight into the edge until in the middle part. Once the cutting and trimming of sponge done, carefully insert the germinated seedlings.
Step 2: Place the mesh pot in the plant holder
Once the germinated seedlings transferred to the mesh pot, place the all mesh pot to the plant holder.
Procedure: Get a clear plastic box container, get the cover and make a holes that suit for mesh pot size to serve as plant holder. The clear box container will be use for water storage with mixture calibrated pH solution and nutrient solution that will be sprayed to the plants roots
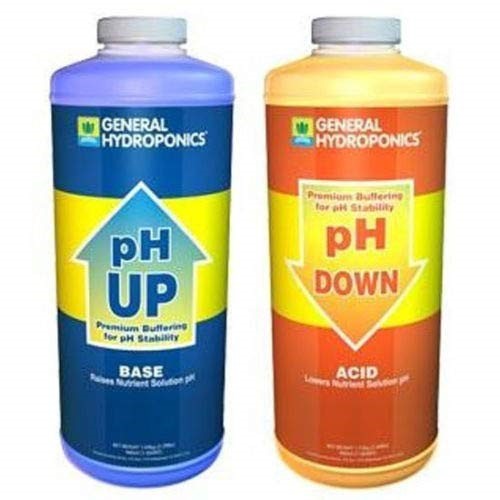
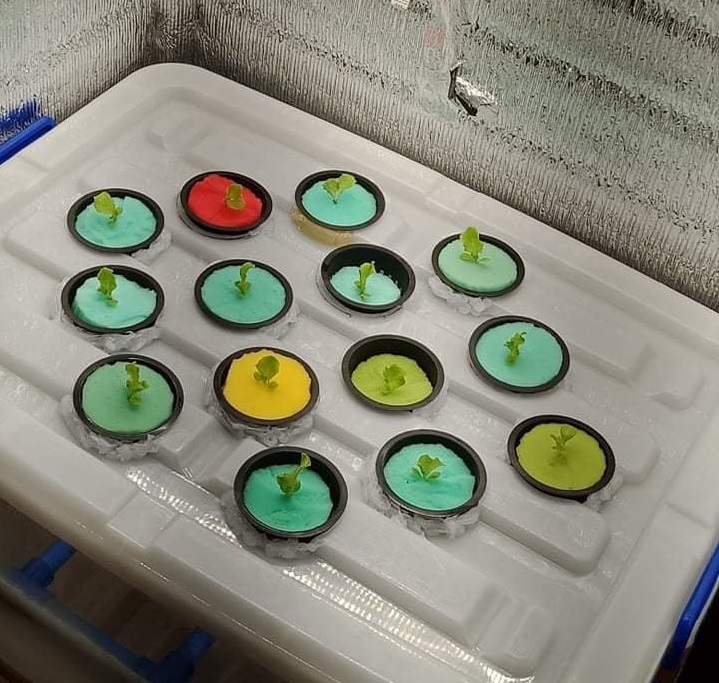

Step 3: Application of pH
pH describes how acidic or basic an aqueous solution is, where a pH below 7 is acidic and a pH greater than 7 is basic. pH of 7 is considered neutral (e.g., pure water). Typically, values of pH range from 0 to 14, although very strong acids may have a negative pH, while very strong bases may have a pH exceeding 14.
A required pH level that need for a plant usually 5.5 – 7 depending on the types and kinds of plants you want. When it comes in lettuce the ideal pH level is 5.5 or 6. Using of prototype it is automatically spay water with mixture of pH solution for the
pH Up – use for raising of acidity once the pH level get down.
pH Down – Use for lowering the acidity of water once the pH level raise.
Step 4: Applying of Nutrient Solution
The application of Nutrient Solution is depend on water level (Liter) on the prototype. Every 1liter of water 2ml of each Nutrient Solution A and B mixed. Using the prototype the mixture if nutrient solution to the water is automatically pump to water container and sprayed to the plant.
Solution A -is rich in calcium which helps the plant against heat stress.
Solution B - contains magnesium which enhances the production of chlorophyll, making it an indispensable building material enabling the plant to grow.

